01
Series 40 Axial Piston Pumps Technical Information General

04
7 Jan 2019
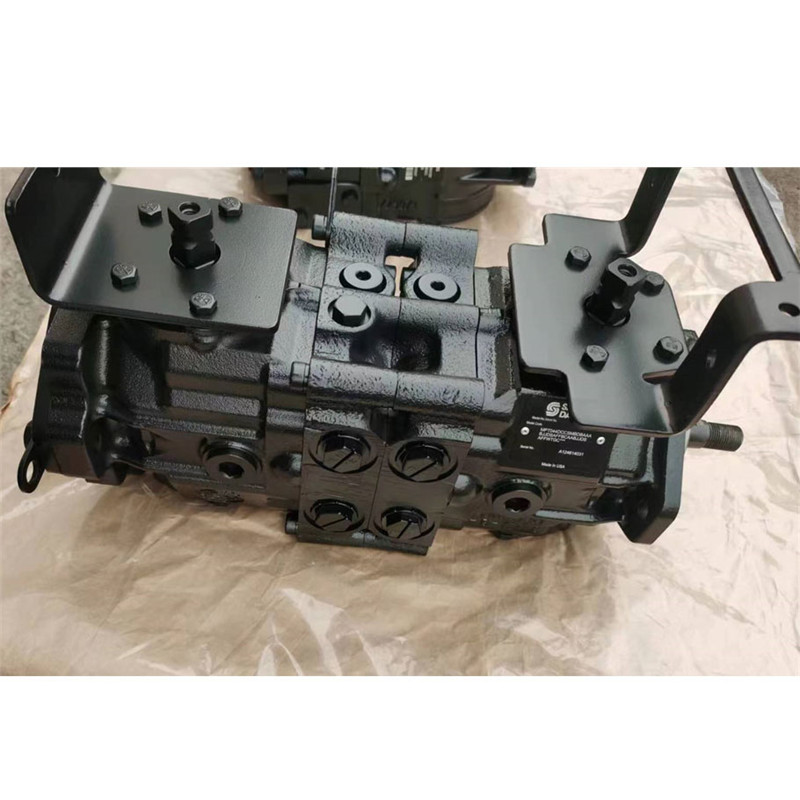
Series 40 is a family of hydrostatic pumps and motors for medium power applications with maximum loads of 345 bar [5000 psi]. These pumps and motors can be applied together or combined with other products in a system to transfer and control hydraulic power.
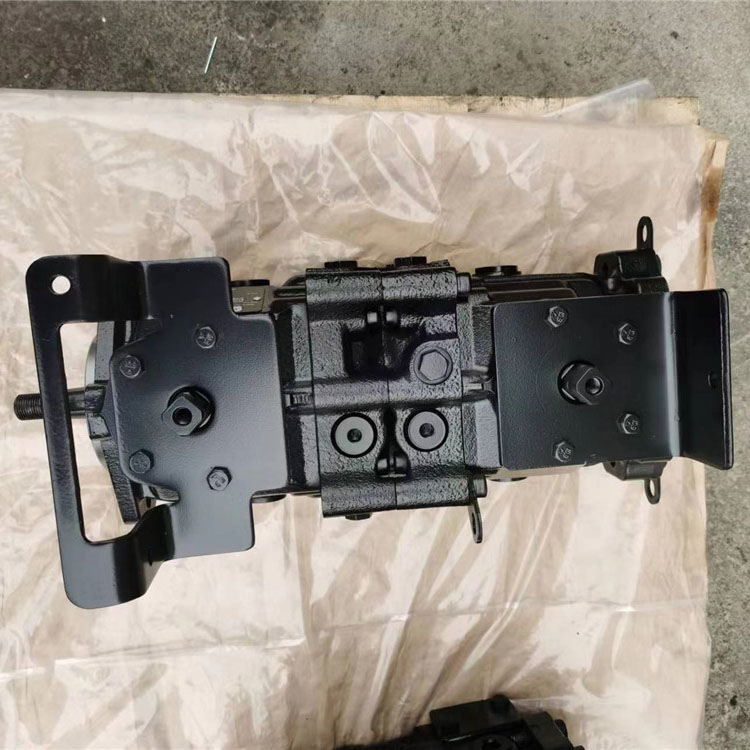
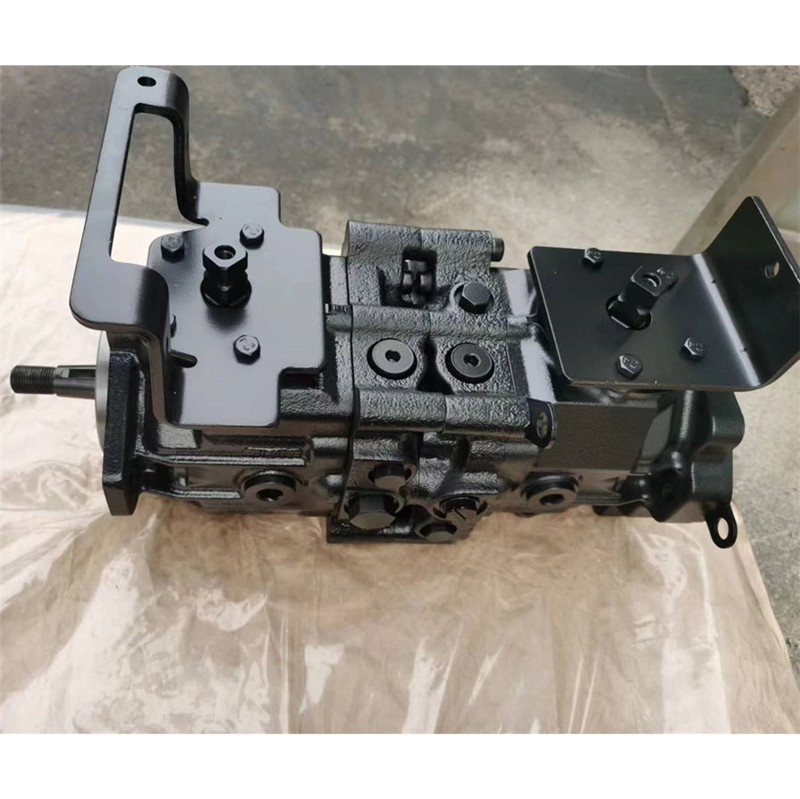
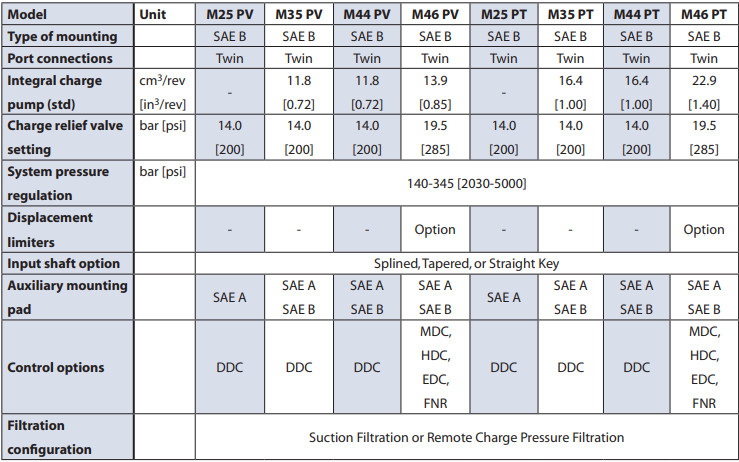
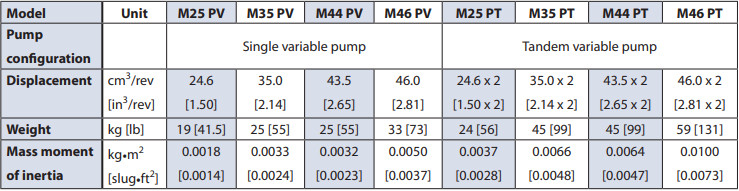
Series 40 pump + motor transmissions provide an infinitely variable speed range between zero and maximum in both forward and reverse modes of operation. The pumps and motors each come in four frame sizes: M25, M35, M44, and M46.
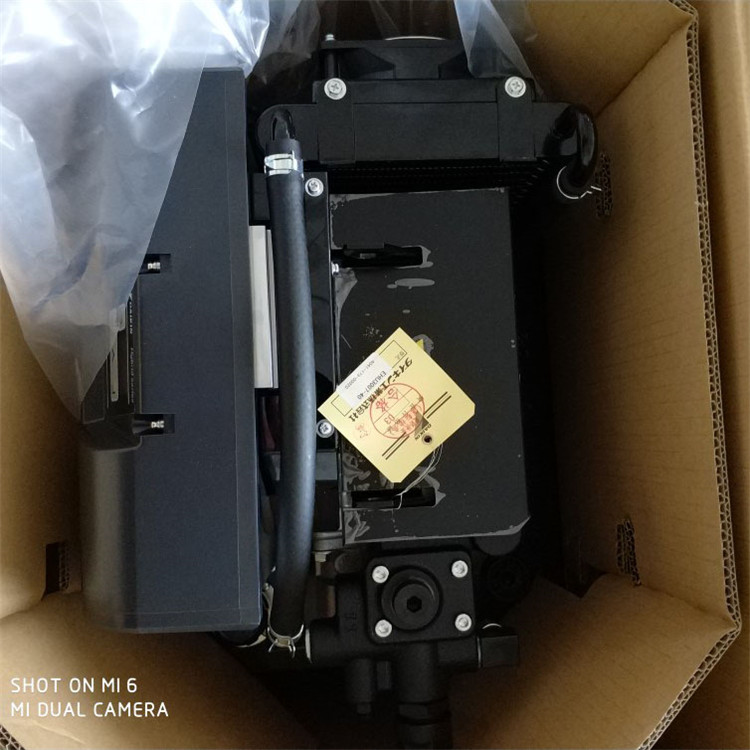
Series 40 pumps are compact, high power density units. All models use the parallel axial piston / slipper concept in conjunction with a tiltable swashplate to vary the pump’s displacement. Reversing the angle of the swashplate reverses the flow of fluid from the pump, reversing the direction of rotation of the motor output.
Series 40 - M35, M44, and M46 pumps may include an integral charge pump to provide system replenishing and cooling fluid flow, as well as servo control fluid flow on M46 pumps. M25 pumps are designed to receive charge flow from an auxiliary circuit or from a gear pump mounted on the auxiliary mounting pad. Series 40 pumps feature a range of auxiliary mounting pads to accept auxiliary hydraulic pumps for use in complementary hydraulic systems.

04
7 Jan 2019
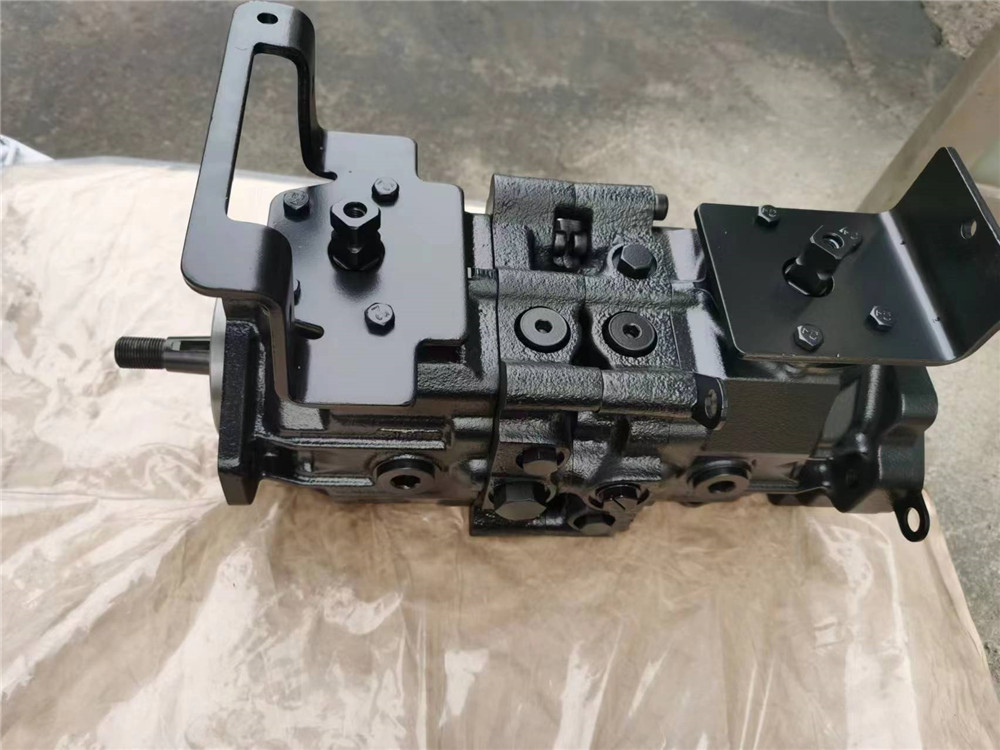
Series 40 - M46 pumps offer proportional controls with either manual, hydraulic, or electronic actuation. An electric three-position control is also available. The M25, M35, and M44 pumps include a trunnion style direct displacement control.
Series 40 motors also use the parallel axial piston / slipper design in conjunction with a fixed or tiltable swashplate. The family includes M25, M35, M44 fixed motor units and M35, M44, M46 variable motor units. For complete technical information on Series 40 motors, refer to Series 40 Motors Technical Information, 520L0636.
The M35 and M44 variable motors feature a trunnion style swashplate and direct displacement control. The M46 variable motors use a cradle swashplate design and a two-position hydraulic servo control.
The M46 variable motor is available in a cartridge flange version, which is designed to be compatible with CW and CT compact planetary gearboxes. This combination provides a short final drive length for applications with space limitations.


04
7 Jan 2019
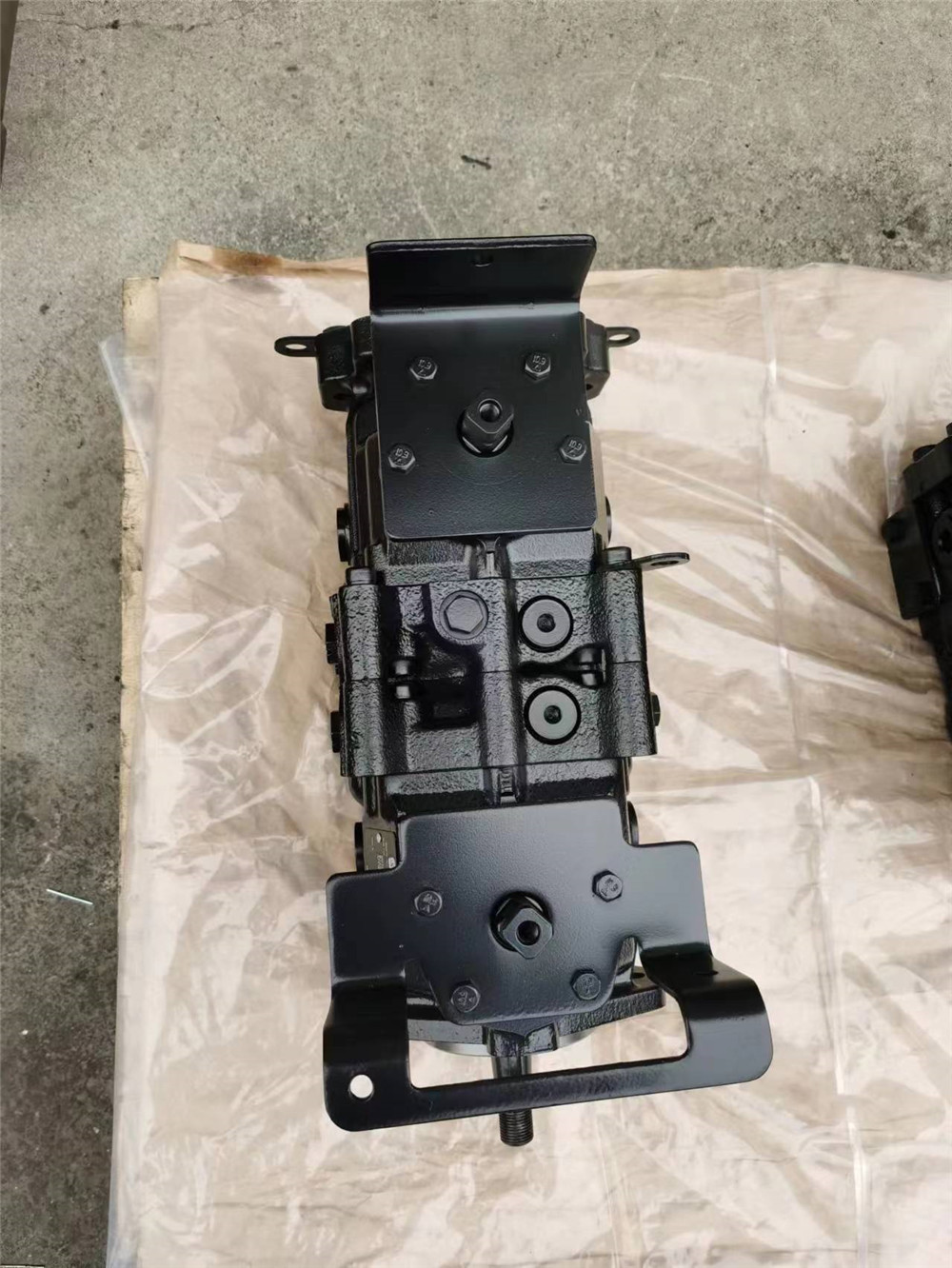
Charge flow is required on all Series 40 units applied in closed circuit installations to make up for internal leakage, maintain positive pressure in the main circuit, provide flow for cooling, replace any leakage losses from external valving or auxiliary systems, and on M46 units, to provide flow and pressure for the control system.
Maintain rated charge pressure under all conditions of operation to prevent damage to the transmission.
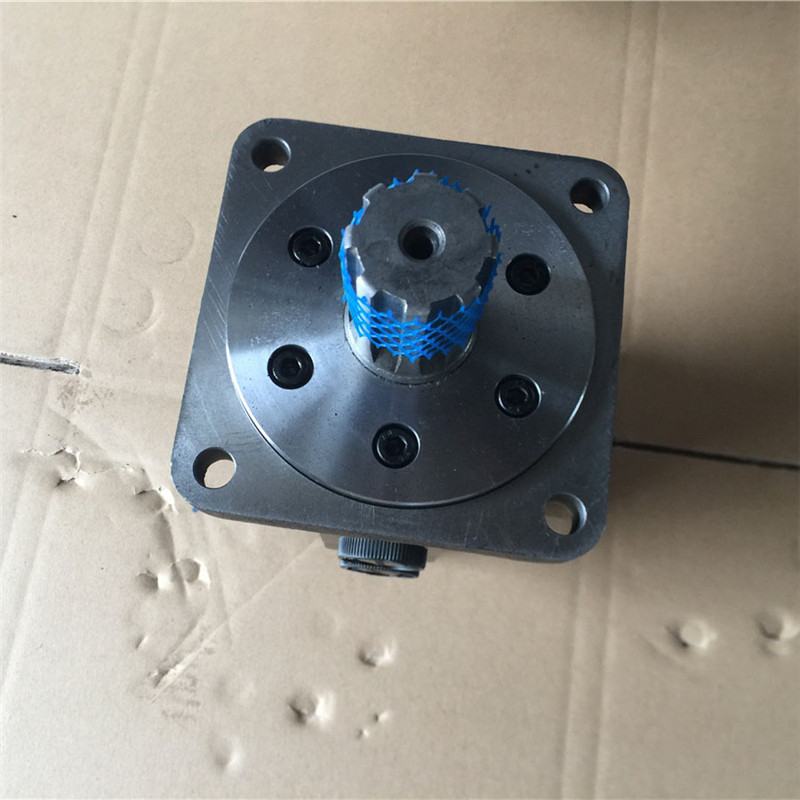
All Series 40 pumps (except M25 pumps) may be equipped with integral charge pumps. These charge pump sizes have been selected to meet the needs of a majority of Series 40 applications.
Many factors influence the charge flow requirements and the resulting charge pump size selection. These factors include system pressure, pump speed, pump swashplate angle, type of fluid, temperature, size of heat exchanger, length and size of hydraulic lines, control response characteristics, auxiliary flow requirements, hydraulic motor type, etc. In most Series 40 applications a general guideline is that the charge pump displacement should be equal to or greater than 10% of the total displacement of all units in the system.
The total charge flow requirement is the sum of the charge flow requirements of each of the components in the system. Use the information provided on the following pages to make a charge pump selection for a given application.

04
7 Jan 2019
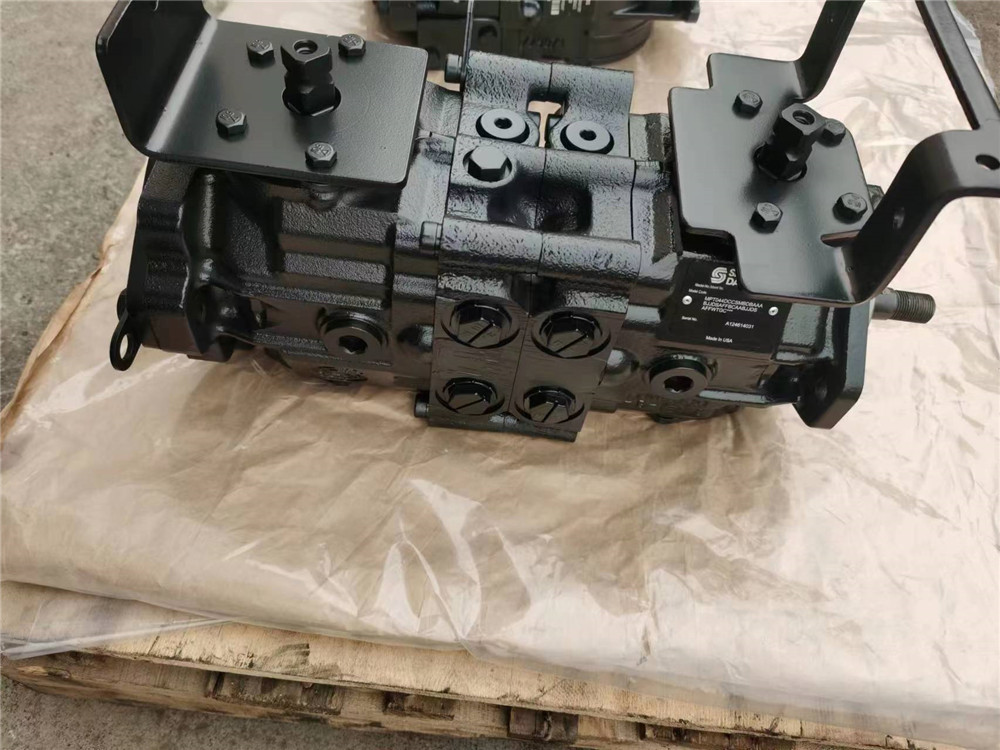
System features and conditions that may invalidate the 10% of displacement rule include (but are not limited to):
• Operation at low input speeds (below 1500 RPM)
• Shock loading • Excessively long system lines
• Auxiliary flow requirements
• Use of low speed high torque motors
If a charge pump of sufficient displacement to meet the 10% of displacement rule is not available or if any of the above conditions exist which could invalidate the 10% rule, contact your Sauer-Danfoss representative. A charge pump sizing worksheet is available in BLN-9885.
M25 pumps do not allow for integral charge pumps. Other Series 40 pumps are also available without charge pumps. When an integral charge pump is not used, an external charge supply is required to ensure adequate charge pressure and cooling










